First we describe some very basic spatial queries and then we will define relatively complex
queries. One or more basic queries may be issued to answer these complex queries. Let  and
and  be two multidimensional spatial data objects (points, lines or regions), below
we define some very basic spatial queries.
be two multidimensional spatial data objects (points, lines or regions), below
we define some very basic spatial queries.
Note that for all of the above queries, the database system does not need to access any other
object from the spatial index. These operations involve geometrical computation based on the information
of the two spatial objects  and
and  . Next we briefly describe the queries that are more
advanced and in order to answer these queries, the database system may need to traverse
spatial indexes or it may need to call few of the basic operations
described above.
. Next we briefly describe the queries that are more
advanced and in order to answer these queries, the database system may need to traverse
spatial indexes or it may need to call few of the basic operations
described above.
- Spatial Range Query(
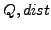 ). Find all the objects that lie within a given distance
). Find all the objects that lie within a given distance 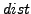 from
the query object
from
the query object  . In other words, find all objects
. In other words, find all objects 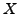 such that DISTANCE(
such that DISTANCE(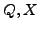 )
)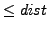 .
For example, find all the restaurants that are within
.
For example, find all the restaurants that are within  km from my current location.
km from my current location.
- Containment Query(
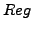 ). Find all the data objects that lie within the query region
). Find all the data objects that lie within the query region
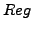 . Formally, return all the objects
. Formally, return all the objects 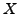 for which CONTAINS(
for which CONTAINS(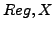 ) returns true. For example,
find all the aeroplanes that are currently in New York.
) returns true. For example,
find all the aeroplanes that are currently in New York.
- Exact Match Query(
 ): Find all objects that have same spatial extent as the object
): Find all objects that have same spatial extent as the object  has. More specifically,
find all the spatial objects
has. More specifically,
find all the spatial objects 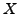 for which EQUALS(
for which EQUALS(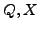 ) returns true. Consider, for an example, a
query may be issued to find a house that has same structure as my house.
) returns true. Consider, for an example, a
query may be issued to find a house that has same structure as my house.
- Nearest Neighbor Query(
 ). Find the closest object to the query object
). Find the closest object to the query object  . The problem
may also be extended to
. The problem
may also be extended to 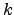 nearest neighbor (
nearest neighbor (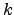 NN) query, that is to find
NN) query, that is to find 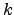 closest objects to the
query object. More specifically, a
closest objects to the
query object. More specifically, a 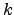 nearest neighbor query is to find a set of objects
nearest neighbor query is to find a set of objects  that contains
that contains 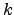 objects such that for all
objects such that for all 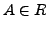 and for all other objects
and for all other objects  ,
,
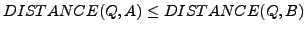 . Note that the answer may change depending on the distance definition.
Fig.
. Note that the answer may change depending on the distance definition.
Fig. ![[*]](./icons/crossref.png) illustrates this. The nearest neighbor of
illustrates this. The nearest neighbor of  is
is  if the distance between
two points is defined as the minimum distance between them. If the distance is
defined as the maximum distance between the two objects,
if the distance between
two points is defined as the minimum distance between them. If the distance is
defined as the maximum distance between the two objects,  becomes the nearest neighbor of
becomes the nearest neighbor of  .
.
Figure:
Effect of Different Distance Definitions on Nearest Neighbors
|
|
One example of such queries is to find  closest gas stations to my current location. Also note
that other metrics than Euclidean distance may also be used. In above example, the road
distance may be used to find the nearest neighbors.
closest gas stations to my current location. Also note
that other metrics than Euclidean distance may also be used. In above example, the road
distance may be used to find the nearest neighbors.
- Spatial Join Query(
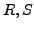 ). Let
). Let  and
and 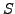 be two sets of objects, a spatial join query
is to find object pairs from these sets so that they satisfy some specified join predicate. The examples of possible join
predicates may include INTERSECTS, DISJOINT, DISTANCE and CONTAINS operations defined above. An example of such
queries is to find all hotel-cinema pairs so that distance between them is less that
be two sets of objects, a spatial join query
is to find object pairs from these sets so that they satisfy some specified join predicate. The examples of possible join
predicates may include INTERSECTS, DISJOINT, DISTANCE and CONTAINS operations defined above. An example of such
queries is to find all hotel-cinema pairs so that distance between them is less that  km.
km.
Muhammad Aamir Cheema
2007-10-11
![]() and
and ![]() be two multidimensional spatial data objects (points, lines or regions), below
we define some very basic spatial queries.
be two multidimensional spatial data objects (points, lines or regions), below
we define some very basic spatial queries.
![]() and
and ![]() . Next we briefly describe the queries that are more
advanced and in order to answer these queries, the database system may need to traverse
spatial indexes or it may need to call few of the basic operations
described above.
. Next we briefly describe the queries that are more
advanced and in order to answer these queries, the database system may need to traverse
spatial indexes or it may need to call few of the basic operations
described above.